The process consumers use to buy products and services is different for every individual and every category of product. However, we have been able to categorize this behavior based on their degree of involvement, and the degree of difference between the brands in the product category. There are four types of Buying Behavior:
1) Complex Buying Behavior - Has high involvement with significant levels of differences between brands.
2) Variety-seeking Buying Behavior - Has low involvement with significant levels of differences between brands.
3) Dissonance-reducing Buying Behavior - Has high involvement with very few differences between brands.
4) Habitual Buying Behavior - Has very low levels of involvement and very few differences between brands.
Let's start by examining Complex Buying Behavior.
Complex Buying Behavior
Complex Buying Behavior defines buying scenarios that are characterized by high levels of consumer "involvement" in a purchase decision; with significant amounts of perceived differences between brands in the product category. Involvement refers to actions the consumer must take to understand the product or service they are motivated to buy. When high involvement is necessary, the consumer does whatever they can to learn: research, read reviews, talk to others, and "test drive" different models at retail locations.
High involvement tends to be associated with products that are more expensive, infrequently purchased, technologically advanced, and highly expressive of the buyer's personality profile.
The involvement process helps the consumer understand the differences between the brands of products they are motivated to buy. This process is where the consumer develops (and sometimes changes) their beliefs and attitudes. These beliefs and attitudes, along with their buying motives, will influence the consumer's decision.
Marketers of high-involvement products need to have an understanding of the buying process. It is their job to help the consumer learn about their product, and create messaging that influences the buyer's beliefs and attitudes about competitor's products. Understanding your target customer's Personality Profile is a key component of your marketing plan.
Follow @macdailybites
Pages - Menu
▼
Pages
▼
Tuesday, December 4, 2012
Tuesday, November 27, 2012
Marketing 101: Pyschological Factors of Consumer Buyer Behavior
Consumers are complicated. If they bought things based on only a select criteria, then it would be easy to convince others to buy our products and services. There would be no need for elaborate ad campaigns and large advertising budgets. Unfortunately, consumers are influenced by many different stimuli, and they use many different factors to decide what to buy and when to buy it. One of the major influencers of consumer buyer behavior is the consumer's own unique personality.
When we study personality, we are examining the unique psychological characteristics that create relatively consistent, lasting behavior in response to the consumer's environment. We usually refer to someone's personality by traits, such as self-confidence, dominance, sociability, autonomy, defensiveness, adaptability, and aggressiveness. Personality is extremely important, because it allows us to build a profile of our customer. It allows us to really understand who they are, and why they buy. You can use that profile to better understand how to tailor your products and services to that buyer, and tailor your messaging to be as affective as possible when selling to that customer segment.
Consumers aren't the only ones who can have personalities and profiles. So can brands. Brand personalities are the specific mix of human traits that may be attributed to that brand. In order to better associate our brands with our target customers, we try to give them personalities that are relatable. We use these personalities to tailor the look and perception of the brand and its messaging in the marketplace so that we can attract specific consumers to our products and services.
Self Concept
Many marketers use a concept related to personality, called Self-Concept. The main premise of self-concept is that a consumer's possessions directly contribute to, and directly reflect their identities. Basically a person "is" what they have. Therefore, marketers try to understand our target customers by the things that they own and the things that they buy.
When we know the buyer's personality, when we have defined our brand personality, and when we have attempted to understand our consumer buy their existing buying patterns, we then combine all of this along with specific psychological factors to better understand their buyer behavior. Currently we look to four specific factors of our target customers when building their personality profile:
1) Motivation
2) Perception
3) Learning
4) Beliefs and Attitudes
Let's examine these one by one.
Motivation
A motive is a need that has become so sufficiently pressing that it directs the consumer to seek satisfaction of that need. A consumer has a number of needs at any given time of their life. Humans are constantly being influenced by various biological and psychological motivations. Many common biological needs arise from various states of "tension", such as hunger, thirst, or some form of physical discomfort. Psychological needs will arise from a desire for social recognition, esteem, or belonging in familial, social, or political groups. If one of these motivations becomes strong enough within the consumer, it "becomes" a need.
Through various research marketers have identified five "categories" of motivational needs:
1) Self-Actualization: a consumer's self-development and realization
2) Esteem: a consumer's sense of self-esteem, self-recognition, and social/economic status in the world
3) Social: a consumer's sense of belonging and feeling loved in their environment
4) Satisfaction: a consumer's sense of security and level of protection in their environment
5) Physiological: a consumer's basic need for food, water and shelter
Marketer's have found that there tends to be a hierarchy of need satisfaction within the typical human being: Physical needs must be satisfied first, then a person is willing to seek satisfaction fulfillment, then a person will approach social needs, then a person will pursue esteem, and then finally self-actualization within their environment. The basic principle here is that a consumer will almost always try to satisfy the most "pressing" needs first above anything else. When that need is met, it will stop being a motivator, and the consumer will "move on" to the next most influential motivator in the hierarchy of needs.
Marketers need to remember that motivated people are ready to buy. Use that to your advantage.
Perception
How a consumer determines what they will buy is heavily influenced by their perception of the situation they are in at that moment in time. Perception is the process by which consumers select, organize, and interpret information and environmental stimuli in order to form a more meaningful picture of the world around them.
One of the most massive forms of environmental stimuli is advertising. On average, consumers are exposed to 3000 - 5000 advertisements everyday. It is physically impossible for a consumer's brain to actively pay attention to all of that stimuli. Add to that all of the other environmental stimuli around them: smells, tastes, sounds, conversations; it's a wonder that humans are able to concentrate on anything at all. As a result, the brain controls what stimuli it will engage with. It is this process that creates perception. Consumers form their perceptions through the brain's distinct processes of selective attention, selective distortion, and seletice retention.
1) Selective Attention is the tendency for consumers to screen out most of the information they are exposed to. We have to work very hard to get the consumer's attention.
2) Selective Distortion: Every consumer fits incoming stimuli into their own mind-set - through their own set of "rose colored glasses". Selective distortion is the tendency of people to interpret information in a way that will support what they already believe, or what they want to believe.
3) Selective Retention: Consumers will usually forget much of the stimuli they have been exposed to. Consumers will usually store the information that best supports their existing attitudes and beliefs (or the ones they want to have), so selective retention allows them "remember" the good points they favor and "forget" the negative points that have been made about other brands that they don't like.
These processes are why marketers use so much repetition in their advertising campaigns. We have to battle our way into the minds of the consumer, force our way in, and in the end, convince the mind of the consumer that our message is the right one to pay attention to.
Learning
When people perform an activity, they are actively learning. Most learning theorists believe that the majority of human behavior is "learned" behavior. Consumer buyer behavior is a partly learned behavior. Consumers "learn" their buyer behavior through drives, cues, responses, and reinforcement. Each one of these builds upon the other.
Drives are strong internal stimuli inside the consumer's mind that create calls for action. These calls for action, if strong enough, will create a motive (see above), and lead the consumer to attempt to move towards an object of stimuli. That object usually will be what satisfies the need.
Drives create Cues. Cues refer to more "minor" stimui that condition the consumer's behavior. Cues help the consumer decide when, where, and how to respond to a drive.
Responses are the consumer's actions based off of drives, motives, and cues from environmental stimuli.
Responses build Reinforcement, which influences the consumer's future buyer behavior. If the purchase experience and immediate experience with the product has been positive, then the consumer will likely consider buying that same product in the future. If the consumer's experience is somewhat negative, then they are likely to seek a different product later when the need has to be fulfilled again.
Beliefs and Attitudes
Through our daily activities, we build beliefs and attitudes that in turn influence our buying behavior.
A consumer's beliefs are descriptive thoughts that they have about something, while attitudes are a consumer's "relatively" consistent evaluations, feelings, and tendencies toward an object or idea. Attitudes put people into specific frames of mind, and help to move them towards or away from certain products and brands. Unfortunately attitudes can be very difficult to change. Attitudes are a part of a consumer's learned behavior patterns. Changing a consumer's attitudes and beliefs usually will require us try to change many other perceptions and attitudes in other areas of the consumer's mind. Often it is easier to position a product into an existing attitude, than to fight against them and try to change them.
Marketers need to understand these beliefs and attitudes in order to best position their messaging in front of the target consumer. If we believe some of the target consumer's beliefs and attitudes are wrong about us, thereby preventing sales, then we can understand how to launch focused messaging campaigns to change beliefs about our products and brands.
Consumers are complicated. Their unique personalities have many facets, and all of them are involved in what is hardly a simple decision when they are choosing to buy something. It is the marketer's responsibility to do their due diligence and learn as much as possible about their target customer. Failing to have some understanding of the pyschological factors of consumer buyer behavior will result in unfocused messaging, and wasted marketing dollars. Today's economic reality forces us to do enough research before starting any creative for our ad campaigns.
Follow @macdailybites
When we study personality, we are examining the unique psychological characteristics that create relatively consistent, lasting behavior in response to the consumer's environment. We usually refer to someone's personality by traits, such as self-confidence, dominance, sociability, autonomy, defensiveness, adaptability, and aggressiveness. Personality is extremely important, because it allows us to build a profile of our customer. It allows us to really understand who they are, and why they buy. You can use that profile to better understand how to tailor your products and services to that buyer, and tailor your messaging to be as affective as possible when selling to that customer segment.
Consumers aren't the only ones who can have personalities and profiles. So can brands. Brand personalities are the specific mix of human traits that may be attributed to that brand. In order to better associate our brands with our target customers, we try to give them personalities that are relatable. We use these personalities to tailor the look and perception of the brand and its messaging in the marketplace so that we can attract specific consumers to our products and services.
Self Concept
Many marketers use a concept related to personality, called Self-Concept. The main premise of self-concept is that a consumer's possessions directly contribute to, and directly reflect their identities. Basically a person "is" what they have. Therefore, marketers try to understand our target customers by the things that they own and the things that they buy.
When we know the buyer's personality, when we have defined our brand personality, and when we have attempted to understand our consumer buy their existing buying patterns, we then combine all of this along with specific psychological factors to better understand their buyer behavior. Currently we look to four specific factors of our target customers when building their personality profile:
1) Motivation
2) Perception
3) Learning
4) Beliefs and Attitudes
Let's examine these one by one.
Motivation
A motive is a need that has become so sufficiently pressing that it directs the consumer to seek satisfaction of that need. A consumer has a number of needs at any given time of their life. Humans are constantly being influenced by various biological and psychological motivations. Many common biological needs arise from various states of "tension", such as hunger, thirst, or some form of physical discomfort. Psychological needs will arise from a desire for social recognition, esteem, or belonging in familial, social, or political groups. If one of these motivations becomes strong enough within the consumer, it "becomes" a need.
Through various research marketers have identified five "categories" of motivational needs:
1) Self-Actualization: a consumer's self-development and realization
2) Esteem: a consumer's sense of self-esteem, self-recognition, and social/economic status in the world
3) Social: a consumer's sense of belonging and feeling loved in their environment
4) Satisfaction: a consumer's sense of security and level of protection in their environment
5) Physiological: a consumer's basic need for food, water and shelter
Marketer's have found that there tends to be a hierarchy of need satisfaction within the typical human being: Physical needs must be satisfied first, then a person is willing to seek satisfaction fulfillment, then a person will approach social needs, then a person will pursue esteem, and then finally self-actualization within their environment. The basic principle here is that a consumer will almost always try to satisfy the most "pressing" needs first above anything else. When that need is met, it will stop being a motivator, and the consumer will "move on" to the next most influential motivator in the hierarchy of needs.
Marketers need to remember that motivated people are ready to buy. Use that to your advantage.
Perception
How a consumer determines what they will buy is heavily influenced by their perception of the situation they are in at that moment in time. Perception is the process by which consumers select, organize, and interpret information and environmental stimuli in order to form a more meaningful picture of the world around them.
One of the most massive forms of environmental stimuli is advertising. On average, consumers are exposed to 3000 - 5000 advertisements everyday. It is physically impossible for a consumer's brain to actively pay attention to all of that stimuli. Add to that all of the other environmental stimuli around them: smells, tastes, sounds, conversations; it's a wonder that humans are able to concentrate on anything at all. As a result, the brain controls what stimuli it will engage with. It is this process that creates perception. Consumers form their perceptions through the brain's distinct processes of selective attention, selective distortion, and seletice retention.
1) Selective Attention is the tendency for consumers to screen out most of the information they are exposed to. We have to work very hard to get the consumer's attention.
2) Selective Distortion: Every consumer fits incoming stimuli into their own mind-set - through their own set of "rose colored glasses". Selective distortion is the tendency of people to interpret information in a way that will support what they already believe, or what they want to believe.
3) Selective Retention: Consumers will usually forget much of the stimuli they have been exposed to. Consumers will usually store the information that best supports their existing attitudes and beliefs (or the ones they want to have), so selective retention allows them "remember" the good points they favor and "forget" the negative points that have been made about other brands that they don't like.
These processes are why marketers use so much repetition in their advertising campaigns. We have to battle our way into the minds of the consumer, force our way in, and in the end, convince the mind of the consumer that our message is the right one to pay attention to.
Learning
When people perform an activity, they are actively learning. Most learning theorists believe that the majority of human behavior is "learned" behavior. Consumer buyer behavior is a partly learned behavior. Consumers "learn" their buyer behavior through drives, cues, responses, and reinforcement. Each one of these builds upon the other.
Drives are strong internal stimuli inside the consumer's mind that create calls for action. These calls for action, if strong enough, will create a motive (see above), and lead the consumer to attempt to move towards an object of stimuli. That object usually will be what satisfies the need.
Drives create Cues. Cues refer to more "minor" stimui that condition the consumer's behavior. Cues help the consumer decide when, where, and how to respond to a drive.
Responses are the consumer's actions based off of drives, motives, and cues from environmental stimuli.
Responses build Reinforcement, which influences the consumer's future buyer behavior. If the purchase experience and immediate experience with the product has been positive, then the consumer will likely consider buying that same product in the future. If the consumer's experience is somewhat negative, then they are likely to seek a different product later when the need has to be fulfilled again.
Beliefs and Attitudes
Through our daily activities, we build beliefs and attitudes that in turn influence our buying behavior.
A consumer's beliefs are descriptive thoughts that they have about something, while attitudes are a consumer's "relatively" consistent evaluations, feelings, and tendencies toward an object or idea. Attitudes put people into specific frames of mind, and help to move them towards or away from certain products and brands. Unfortunately attitudes can be very difficult to change. Attitudes are a part of a consumer's learned behavior patterns. Changing a consumer's attitudes and beliefs usually will require us try to change many other perceptions and attitudes in other areas of the consumer's mind. Often it is easier to position a product into an existing attitude, than to fight against them and try to change them.
Marketers need to understand these beliefs and attitudes in order to best position their messaging in front of the target consumer. If we believe some of the target consumer's beliefs and attitudes are wrong about us, thereby preventing sales, then we can understand how to launch focused messaging campaigns to change beliefs about our products and brands.
Consumers are complicated. Their unique personalities have many facets, and all of them are involved in what is hardly a simple decision when they are choosing to buy something. It is the marketer's responsibility to do their due diligence and learn as much as possible about their target customer. Failing to have some understanding of the pyschological factors of consumer buyer behavior will result in unfocused messaging, and wasted marketing dollars. Today's economic reality forces us to do enough research before starting any creative for our ad campaigns.
Follow @macdailybites
Tuesday, October 23, 2012
Marketing 101: The VALS Study
As marketers are certainly aware, a consumer's economic situation will undoubtedly affect their purchasing decisions in some way. Marketers of income-sensitive products and services should be watching for changes in a demographic's income, savings and access to the prevailing interest rates. If financial trends are towards a recession, we should be making proactive changes to alter our product and service lines, or reposition the messaging of our campaigns. During good economies, we should be doing the same. The point is, our messaging, and our products, should be CONSTANTLY evolving to best reflect the consumer's buying environment.
Marketer's need to remember that although consumers in a chosen demographic may be coming from the same subculture, social class and occupation, they will usually have very different lifestyles. It is our job to understand these lifestyles so we can tailor our messaging as best as possible to convince the consumer that our products and services have the right value they are looking for. Recall, a lifestyle is a consumer's pattern of living, and is expressed within their activities, interests and opinions. Activities, Interests, and Opinions are commonly referred to as AIO Dimensions. These AIO Dimensions are usually defined as:
- Activities: work, hobbies, shopping, sports, social events
- Interests: food, fashion, family and recreation
- Opinions: about themselves, social issues, business, products
Lifestyle is more than a social class or a consumer's personality, it encompasses a consumer's patterns of action and their interaction with the world around them. When utilized affectively, the lifestyle concept helps us understand changing consumer values and how they affect consumer buyer behavior.
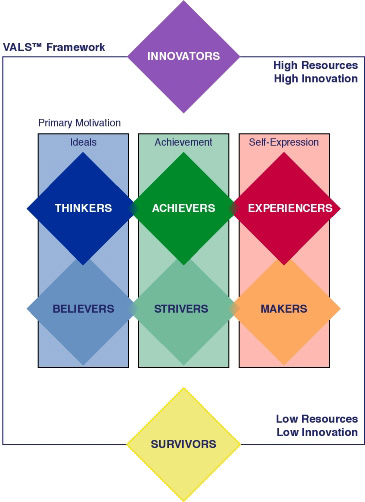
The most widely used lifestyle classification system is the VALS study. VALS classifies people by their psychological characteristics via four major demographics that correlate with consumer buyer behavior. The VALS study helps us understand how consumers spend their time and money, and it divides consumers into groups we can understand based on their primary motivations and resources.
Primary Motivations are defined by the consumer's ideals, the achievements they are seeking to attain, and their methods of self expression. Consumers that are primarily motivated by ideals are usually guided by knowledge and principles. Consumers that are primarily motivated by achievement tend to look for products and services that demonstrate their success in an outward manner to their peers. Consumers that are primarily motivated by self expression usually desire social or physical activities that provide their lives with variety and some sense of risk.
Resources refers to the consumer's level of economic, education, health, self-confidence, and "energy" resources. In a VALS study you are categorized has having high resources or low resources. The resource classification does not have any regard for a consumer's Primary Motivations. The resource categorization also defines consumers that have extremely high or low resources: Innovators and Survivors. Innovators have so many resources (ie: usually money since it enables so many things) that they will display all of the primary motiavtors to some degree. On the other hand, Survivors have so few resources (ie: economically poor) that they usually show no primary motivations at all. These consumers have to focus on meeting needs and not on fulfilling any of their desires.
There is so much more to say about these different classifications of consumers. Let's dive deeper into the classifications of the VALS study.
Innovators
Innovative consumers are typically defined as sophisticated, successful, "take-charge" people with extremely high self-esteem and self-confidence. Because these consumers have such abundant amounts of resources, they are able to exhibit all three primary motivations at various levels. They are considered to be change and thought leaders. Innovators are usually extremely receptive to new ideas and technologies in the marketplace. Innovators are very active consumers, and their buyer behavior reflects their tastes for upscale, niche products and services. Innovators are very conscious about their "image", however not as an outward appearance of their status or power, but as an individual expression of their tastes, style, independence, and personality. Innovators are usually members of the established and emerging leaders in society, business and government, yet they continue to seek new challenges. They never stand still; they love variety. Their material possessions and recreational activities reflect a preference for the "finer things in life."
Survivors
Survivors live very focused lives. Because they have few resources (mainly economic) with which to exist, these consumers often feel like that the world around them is changing too fast . Survivors are more comfortable with the "familiar" and "traditional", and they are primarily concerned with the safety and security of their families. Because these consumers must focus on meeting needs rather than fulfilling wants and desires, Survivors don't show a strong levels of primary motivations. Out of the necessity of their situations, Survivors are cautious consumers. These consumers represent a very modest market for most products and services. Survivors tend to be loyal to specific, habitually purchased brands, especially if they are at discounted prices.
Thinkers
Thinkers represent consumers motivated by their ideals. These consumers are more mature, more satisfied, more comfortable with themselves, and are highly reflective. Thinkers value order in life, knowledge through educational opportunities, and personal responsibility. Thinkers are usually well educated, and eagerly seek out information to aid in the process of decision making. These consumers keep up with current events. Thinkers have a moderate respect for institutions of authority and social decorum, but they are always open to entertain new ideas. Even though Thinkers usually have incomes that enable them the freedom to satisfy many desires, they tend to be conservative, practical consumers. Thinkers look for durability, functionality, and value in the products that they purchase.
Believers
Like Thinkers, Believers are motivated by ideals. They are conservative, conventional people with concrete beliefs based on traditional, established codes: family, religion, community, and the nation. Many Believers express moral codes that have deep roots and literal interpretation. They follow established routines, organized in large part around home, family, community, and social or religious organizations to which they belong. As consumers, Believers are predictable; they choose familiar products and established brands. They favor U.S. products and are generally loyal customers.
Achievers
Motivated by the desire for achievement, Achievers have goal-oriented lifestyles and a deep commitment to career and family. Their social lives reflect this focus and are structured around family, their place of worship, and work. Achievers live conventional lives, are politically conservative, and respect authority and the status quo. They value consensus, predictability, and stability over risk, intimacy, and self-discovery. With many wants and needs, Achievers are active in the consumer marketplace. Image is important to Achievers; they favor established, prestige products and services that demonstrate success to their peers. Because of their busy lives, they are often interested in a variety of time-saving devices.
Strivers
Strivers are trendy and fun loving consumers. Because they are motivated by achievements, Strivers are concerned about the opinions and approval of others. Money defines success for Strivers, who don't ever seem to have enough of it to meet their desires (which can become viewed as needs for them). These consumers prefer stylish trendy products that give the appearance of the lifestyle of people with greater material riches. Many Strivers see themselves as having a job rather than a career, and a lack of skills, education and focus often prevents these consumers from moving ahead. However, Strivers are active consumers, because for them shopping is a social activity and an opportunity to show off to people in their circle of influence their ability to buy. Strivers are as impulsive as their financial circumstance will allow them to be, sometimes to their own economic demise.
Experiencers
Experiencers are consumers that are primarily motivated by self-expression. These are younger, enthusiastic, and impulsive consumers. Experiencers will quickly become enthusiastic about new opportunities, but are equally quick to cool it they cannot get what they want soon, or after they have experienced the "high" once or twice. As such, these consumers will seek variety and excitement, savoring the fresh, the "offbeat", and the risky. Their energy (remember that energy is s resource) finds an outlet in exercise, sports, outdoor recreation, and social activities. They are avid consumers and are willing to spend a high proportion of their income on fashion, entertainment, and socializing activities. Their buying behavior reflects an emphasis on looking good and having trendy things.
Makers
These consumers, like Experiencers, are motivated by self-expression. Makers express themselves and experience the world by working on it - building a house, raising children, fixing a car, or canning vegetables - and have enough skill, education and energy to carry out their endevours successfully. These consumers are highly practical people who have constructive skills and value self-sufficiency and independence. They usually live within a traditional context of family, practical work, and physical recreation and have little interest in what lies outside that lifesyle. Makers are suspicious of new ideas and large institutions such as big business. They are respectful of government authority and organized labor but are often resentful of government intrusion on individual rights. Makers are motivated by the accumulation of material possessions other than those with a practical or useful purpose. Because they prefer value to luxury, they buy basic products that meet their needs on a daily basis.
When sales are trending down, conducting a VALS Study is a great way to find new customer segments to sell to. It is also a great way to understand how to create messaging for these specific customer segments.
Follow @macdailybites
Tuesday, October 2, 2012
Marketing 101: Social Factors Affecting Consumer Buyer Behavior
In my last post I examined the cultural factors influencing consumer buyer behavior. Cultures, subcultures and cultural trends all shape the Model of Consumer Buying Behavior. Another major part of consumer buyer behavior is the element of Social Factors. Human
beings are social. They need people around them to interact with, and to discuss
various issues in order to reach to better solutions and ideas. We all live in a
society of some form, and it is very important for individuals to adhere to the
"laws" and social "regulations" of a community. These Social Factors typically consist of the consumer's small groups, their family, and their social roles and social status.
First let's examine Groups. For the marketer, a social group is defined as having two or more people who will interact to accomplish individual or mutual goals - one of which is usually purchasing a good or service to meet a need or desire. The reality is that a consumer's behavior isn't influenced my just one group; it is influenced by many different groups. We refer to these groups as Reference Groups.
Reference groups influence the consumer by serving as direct (face to face) or indirect points of comparison or "reference" in building a consumer's behavior and attitudes. In a reference group with direct influence, several individuals may be a part of the consumer's purchase decision. The typical roles of these individuals are:
The Initiator
The Influencer
The Decider
Buyer
User
The User is the person (or persons) who will actually use the product or
service that has been bought.
It is important to note that very often consumers are influenced by reference groups that they do not belong to. We will sometimes refer to these groups as aspirational groups. One example of an aspirational group would be the olympic team of the consumer's country. The consumer may aspire, due to the success of the team members, to "be like them." This may lead them to buy many of the same products that the team members may be endorsing, so that they can move towards their goal of acquiring many of the same traits of those group members. Aspirational groups can exert a lot of influence over a group of consumers, and their potential to help a marketer increase sales should not be ignored.
Family Groups
Family Groups are usually considered to be the most important “buying” organisations within a given society. Marketers are most interested in the roles and influence different members of a family group on a large variety of products and services a consumer may buy. Over time the buying roles of the traditional husband-wife model relationship have been changing. In most societies, the wife is usually the primary buyer for the family unit, primarily in the product categories of food, household products and clothing. However, with more women entering into full-time work, and more men becoming telecommuting, traditional family roles are changing. The challenge for the marketer is understanding how these societal changes affect demand for their products and services, and how the messaging mix might need to be changed to attract male rather than female buyers in a given product category (or vice versa).
Another factor to consider in Family Groups is the stage of life of its members. Married individuals tend to show strong desires towards buying products and services which would benefit not only them but also the members of their family group. A consumer who has a spouse and child at home usually will buy for them rather than spending on themselves. An consumer entering into marriage would be more interested in buying a house, a car, and other household items such as furniture and decorating products. Every consumer will usually go through a common set of stages of life, and will show a different buying mindset in each stage. For a common male consumer this tends to look like:
Social Status
One aspect of social status is a consumer's economic status. Marketers take into consideration the social class of the consumer when tailoring messaging to them. A social class is a relatively "permanent" and ordered division in a society whose members share similar values, interests, and behaviors. These classes have their own distinct reference groups, and often reference groups in some classes will influence consumers who are members of a different social class. Different social classes will tend to desire different categories of products as part of their consumer buyer behavior. For example, an upper middle class consumer will tend to spend more of their disposable income on "luxury" items, whereas a consumer from middle to lower income groups will tend to purchase items that are required for their own survival over day-to-day comfort.
In the United States, there are four distinct class groups:
- Upper Uppers: The social elite who live on inherited wealth. They are philanthropic, own many homes, and send their children to the best schools.
- Lower Uppers: Consumers who earn high income through great ability. They are active in social and political culture groups, buy expensive homes, educations and vehicles.
Middle Class (44%)
- Upper Middles: Professionals and corporate managers who don't have a high family status or unusual levels of wealth. They believe in higher education, and they want the "better things in life".
- Middle Class: "Average" income white and blue collar consumers who live in the better part of town. They buy products to keep up with current trends. They want to be in a nice home in a nice area and send their kids to quality schools.
Working Class (38%)
- They lead a working class lifestyle at any income level, education level, or job. They usually will depend on relatives for economic and emotional support, for purchasing advice, and for assistance in rough times. Family is the most important reference and cultural group.
Lower Class (16%)
- Upper Lowers: These are the working poor. Their living standard is just above the poverty line, and they actively strive to advance to a higher class of life. Often they do not a great education or skills, and they are often poorly paid for unskilled work and tasks.
- Lower Lowers: These are the visibly poor in society. They are poorly educated and unskilled. They are usually out of work and depend on the government for assistance most of the time. They are in the middle of a day-to-day existence.
It is the marketer's job to not ignore any of the reference groups of our target markets. We must be constantly researching and identifying these groups, because they will expose people to new lifestyles and behaviors, and change their attitudes and influence the consumer's self-image. Reference groups are a vital component of our marketing campaigns.
In my next post I will examine other types of social factors. After that I will look at the VALS Lifestyle Classification System.
Follow @macdailybites
First let's examine Groups. For the marketer, a social group is defined as having two or more people who will interact to accomplish individual or mutual goals - one of which is usually purchasing a good or service to meet a need or desire. The reality is that a consumer's behavior isn't influenced my just one group; it is influenced by many different groups. We refer to these groups as Reference Groups.
Reference groups influence the consumer by serving as direct (face to face) or indirect points of comparison or "reference" in building a consumer's behavior and attitudes. In a reference group with direct influence, several individuals may be a part of the consumer's purchase decision. The typical roles of these individuals are:
The Initiator
The Initiator is the individual that first suggests or thinks of the idea of buying
a product or service.
The Influencer
The Influencer is the individual whose view or advice influences the consumer's buying decision. This person is sometimes also referred to as the Opinion Leader. The Influencer is usually has special
skills or knowledge, personality or other characteristics that will exert
social influence on other members of the group. The role of the Influencer or Opinion Leader has taken on a whole new meaning and emphasis with
the advent of social media platforms.
The Decider
The Decider is an individual with power and/or the financial authority
to make the choice regarding which product to buy. This is usually the consumer, but it can also be another person.
Buyer
The Buyer is a person who conducts the buying transaction. This is also usually the consumer, but it can be another person as well.
User
It is important to note that very often consumers are influenced by reference groups that they do not belong to. We will sometimes refer to these groups as aspirational groups. One example of an aspirational group would be the olympic team of the consumer's country. The consumer may aspire, due to the success of the team members, to "be like them." This may lead them to buy many of the same products that the team members may be endorsing, so that they can move towards their goal of acquiring many of the same traits of those group members. Aspirational groups can exert a lot of influence over a group of consumers, and their potential to help a marketer increase sales should not be ignored.
Family Groups
Family Groups are usually considered to be the most important “buying” organisations within a given society. Marketers are most interested in the roles and influence different members of a family group on a large variety of products and services a consumer may buy. Over time the buying roles of the traditional husband-wife model relationship have been changing. In most societies, the wife is usually the primary buyer for the family unit, primarily in the product categories of food, household products and clothing. However, with more women entering into full-time work, and more men becoming telecommuting, traditional family roles are changing. The challenge for the marketer is understanding how these societal changes affect demand for their products and services, and how the messaging mix might need to be changed to attract male rather than female buyers in a given product category (or vice versa).
Another factor to consider in Family Groups is the stage of life of its members. Married individuals tend to show strong desires towards buying products and services which would benefit not only them but also the members of their family group. A consumer who has a spouse and child at home usually will buy for them rather than spending on themselves. An consumer entering into marriage would be more interested in buying a house, a car, and other household items such as furniture and decorating products. Every consumer will usually go through a common set of stages of life, and will show a different buying mindset in each stage. For a common male consumer this tends to look like:
- Bachelorhood: Trends towards alcohol, electronics, vehicles, mobile technology (Spends Lavishly)
- Newly Married: Trends towards purchasing a home, car, furnishings. (Spends sensibly)
- Family with Children: Trends towards purchasing products to secure the well-being of his family’s future.
- Empty Nest (Children getting married)/Retirement/Old Age: Trends towards medicines, health product categories, and products that are part of an increased lifestyle and income level.
Social Status
One aspect of social status is a consumer's economic status. Marketers take into consideration the social class of the consumer when tailoring messaging to them. A social class is a relatively "permanent" and ordered division in a society whose members share similar values, interests, and behaviors. These classes have their own distinct reference groups, and often reference groups in some classes will influence consumers who are members of a different social class. Different social classes will tend to desire different categories of products as part of their consumer buyer behavior. For example, an upper middle class consumer will tend to spend more of their disposable income on "luxury" items, whereas a consumer from middle to lower income groups will tend to purchase items that are required for their own survival over day-to-day comfort.
In the United States, there are four distinct class groups:
- Upper Uppers: The social elite who live on inherited wealth. They are philanthropic, own many homes, and send their children to the best schools.
- Lower Uppers: Consumers who earn high income through great ability. They are active in social and political culture groups, buy expensive homes, educations and vehicles.
Middle Class (44%)
- Upper Middles: Professionals and corporate managers who don't have a high family status or unusual levels of wealth. They believe in higher education, and they want the "better things in life".
- Middle Class: "Average" income white and blue collar consumers who live in the better part of town. They buy products to keep up with current trends. They want to be in a nice home in a nice area and send their kids to quality schools.
Working Class (38%)
- They lead a working class lifestyle at any income level, education level, or job. They usually will depend on relatives for economic and emotional support, for purchasing advice, and for assistance in rough times. Family is the most important reference and cultural group.
Lower Class (16%)
- Upper Lowers: These are the working poor. Their living standard is just above the poverty line, and they actively strive to advance to a higher class of life. Often they do not a great education or skills, and they are often poorly paid for unskilled work and tasks.
- Lower Lowers: These are the visibly poor in society. They are poorly educated and unskilled. They are usually out of work and depend on the government for assistance most of the time. They are in the middle of a day-to-day existence.
It is the marketer's job to not ignore any of the reference groups of our target markets. We must be constantly researching and identifying these groups, because they will expose people to new lifestyles and behaviors, and change their attitudes and influence the consumer's self-image. Reference groups are a vital component of our marketing campaigns.
In my next post I will examine other types of social factors. After that I will look at the VALS Lifestyle Classification System.
Follow @macdailybites
Monday, September 17, 2012
Marketing 101: Cultural Factors Affecting Consumer Purchases
In my last post I discussed the basics of Consumer Buyer Behavior, and I explored the Model of Consumer Buyer Behavior. We are going to continue our discussion by exploring the various characteristics affecting consumer buying behavior. Recall that consumer purchases are not just simple one-and-done affairs. They are affected strongly by cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors. These are all factors that we cannot control, but we have to take them into account or else our marketing is ineffective and money is washed down the drain. Let's begin by examining Cultural Factors.
Cultural Factors
Cultural Factors are some of the strongest influences of consumer buyer behavior. Cultural Factors are the set of basic values, perceptions, wants and behaviors that are "learned" by a consumer from their families and other important social institutions. "Culture" is the most basic source of a consumer's wants and behavior. It lives at the foundation of a consumer's world view. Culture is mostly a learned behavior, being constructed by the society a consumer grows up in. That society "teaches" the consumer basic values, perceptions, wants and behaviors. What a consumer is "taught" can vary greatly in different parts of the world. For example, in the United States a child will learn such values as liberty, democracy, freedom, American Exceptionalism, working hard, making your own success, and family values. Children in many Asian countries will learn such values as social harmony, concern with social and economic well-being instead civil and human rights, loyalty towards authority and the well being of the family over the well being of self.
Marketers need to remember that every group or society has a culture. Cultural influences can and will vary greatly from country to country, social group to social group. If you do not account for these values in your marketing plans, your campaigns could be ineffective, and at worst embarrassing.
Subcultures
Every cultural group has numerous subcultures. Subcultures are groups of people that have a set of shared values based on common life experiences and situations. Subcultures can include different nationalities, religions, racial groups, and geographic regions. Many of these subcultural groups make up important customer segments. Because of this, marketers are designing products and marketing campaigns that are specifically tailored to their needs and wants. An example of a growing customer segment and subculture is the "mature" consumer.
The MetLife Mature Market Institute published a report in 2010 summarizing this growing consumer segment. In 2009 there were over 39 million people over 65 years of age, the majority of which are female. The majority of these people were reported as healthy and active. The top three areas of annual spending were in housing, transportation and food/beverage categories. Armed with basic information such as this, many CMO's are finding opportunities to create new messaging campaigns for existing products to grow sales in this growing customer segment.
Trends
CMO's and marketers need to always try to notice cultural shifts in order to discover new products that might be desired by consumers in other cultures and subcultures. Recent trends that have developed over the past decade are the growth of health and fitness over junk and processed food products, and the personal entertainment market which has grown as group and family entertainment in the living room has decreased (think tablets and Netflix). It is your responsibility to keep an eye on your customer segments, their cultures, subcultures, and any new trends that effect them or may bring new groups of customers to your products. Are you?
Follow @macdailybites
Cultural Factors
Cultural Factors are some of the strongest influences of consumer buyer behavior. Cultural Factors are the set of basic values, perceptions, wants and behaviors that are "learned" by a consumer from their families and other important social institutions. "Culture" is the most basic source of a consumer's wants and behavior. It lives at the foundation of a consumer's world view. Culture is mostly a learned behavior, being constructed by the society a consumer grows up in. That society "teaches" the consumer basic values, perceptions, wants and behaviors. What a consumer is "taught" can vary greatly in different parts of the world. For example, in the United States a child will learn such values as liberty, democracy, freedom, American Exceptionalism, working hard, making your own success, and family values. Children in many Asian countries will learn such values as social harmony, concern with social and economic well-being instead civil and human rights, loyalty towards authority and the well being of the family over the well being of self.
Marketers need to remember that every group or society has a culture. Cultural influences can and will vary greatly from country to country, social group to social group. If you do not account for these values in your marketing plans, your campaigns could be ineffective, and at worst embarrassing.
Subcultures
Every cultural group has numerous subcultures. Subcultures are groups of people that have a set of shared values based on common life experiences and situations. Subcultures can include different nationalities, religions, racial groups, and geographic regions. Many of these subcultural groups make up important customer segments. Because of this, marketers are designing products and marketing campaigns that are specifically tailored to their needs and wants. An example of a growing customer segment and subculture is the "mature" consumer.
The MetLife Mature Market Institute published a report in 2010 summarizing this growing consumer segment. In 2009 there were over 39 million people over 65 years of age, the majority of which are female. The majority of these people were reported as healthy and active. The top three areas of annual spending were in housing, transportation and food/beverage categories. Armed with basic information such as this, many CMO's are finding opportunities to create new messaging campaigns for existing products to grow sales in this growing customer segment.
Trends
CMO's and marketers need to always try to notice cultural shifts in order to discover new products that might be desired by consumers in other cultures and subcultures. Recent trends that have developed over the past decade are the growth of health and fitness over junk and processed food products, and the personal entertainment market which has grown as group and family entertainment in the living room has decreased (think tablets and Netflix). It is your responsibility to keep an eye on your customer segments, their cultures, subcultures, and any new trends that effect them or may bring new groups of customers to your products. Are you?
Follow @macdailybites
Thursday, September 6, 2012
Marketing 101: An Overview of Consumer Buying Behavior
There are many mysteries in life. Love, happiness, success, the meaning of life, teenagers, and for marketing professionals, consumers can be the biggest nut we try to crack and understand on a daily basis. It's our job to understand how to convince our target market to buy what we have to offer. How do we get them to see the value in our messaging so that we can get value from them in return? It all revolves around the "mystery" of consumer buying behavior, and the factors that affect it.
What is Consumer Buyer Behavior? Consumer Buyer Behavior refers to the behavior of the final consumers. These consumers are the individuals and households who are buying goods and services in the marketplace for their own personal consumption. It is important to note that I did not mention the word "business". Consumer Buyer Behavior focuses on B2C transactions, not B2B transactions.
Consumer Buyer Behavior is a "mystery", because consumers vary greatly in their demographics and individual characteristics. No one buyer is alike another. However some groups of buyers do act similarly to each other. In order to study buyer behavior, we have had to create a model to answer the central question of how consumers will respond to different marketing efforts and stimuli. It's called...the "Model of Consumer Buyer Behavior". Original, I know. This stimulus response model is our guide.
The model looks like this:
[1] Consumers "ingest" marketing and other stimuli > [2] the stimuli enters their "buyer black box" > [3] the "black box" creates buyer responses.
It starts with marketing and other stimuli. When we consider marketing stimuli, we usually focus on the "4 P's": Product, Price, Place and Promotion. When we are examining other stimuli, we usually look at internal and outside economic, technological, political and cultural factors that influence the buyer.
All of that stimuli enters what we call the "buyer black box"... the brain. This "black box" contains all of the characteristics of the buyer. The buyer characteristics influence how he or she perceives the marketing stimuli, and creates a reaction. The "black box" also contains the consumer's individual decision process, which is used to evaluate whether or not they will purchase a product.
Finally, this black box creates the "buyer response". This buyer response influences the choice of product, their individual brand choice, the choice of dealer, the timing of the purchase, and the amount of money they will be spent on the goods and services.
Over the next few weeks we will be examining these characteristics as they affect buyer behavior, and discuss the decision process that the consumer follows.
Follow @macdailybites
What is Consumer Buyer Behavior? Consumer Buyer Behavior refers to the behavior of the final consumers. These consumers are the individuals and households who are buying goods and services in the marketplace for their own personal consumption. It is important to note that I did not mention the word "business". Consumer Buyer Behavior focuses on B2C transactions, not B2B transactions.
Consumer Buyer Behavior is a "mystery", because consumers vary greatly in their demographics and individual characteristics. No one buyer is alike another. However some groups of buyers do act similarly to each other. In order to study buyer behavior, we have had to create a model to answer the central question of how consumers will respond to different marketing efforts and stimuli. It's called...the "Model of Consumer Buyer Behavior". Original, I know. This stimulus response model is our guide.
The model looks like this:
[1] Consumers "ingest" marketing and other stimuli > [2] the stimuli enters their "buyer black box" > [3] the "black box" creates buyer responses.
It starts with marketing and other stimuli. When we consider marketing stimuli, we usually focus on the "4 P's": Product, Price, Place and Promotion. When we are examining other stimuli, we usually look at internal and outside economic, technological, political and cultural factors that influence the buyer.
All of that stimuli enters what we call the "buyer black box"... the brain. This "black box" contains all of the characteristics of the buyer. The buyer characteristics influence how he or she perceives the marketing stimuli, and creates a reaction. The "black box" also contains the consumer's individual decision process, which is used to evaluate whether or not they will purchase a product.
Finally, this black box creates the "buyer response". This buyer response influences the choice of product, their individual brand choice, the choice of dealer, the timing of the purchase, and the amount of money they will be spent on the goods and services.
Over the next few weeks we will be examining these characteristics as they affect buyer behavior, and discuss the decision process that the consumer follows.
Follow @macdailybites
Monday, August 27, 2012
Marketing 101: Sampling Plan
In the last Marketing 101 post we examined common Contact Methods for acquiring Primary Data. I listed three traditional methods: telephone, mail, and focus groups. The fact of the matter is that online technologies have completely changed how we as marketing directors and CMO's do our jobs. I truly believe this is for the better. It so so much easier to collect the Primary Data we need via online methods, and it tends to be more cost effective than offline methods. However there are also challenges to online methods, and some of the same issues exist when it comes to the reliability of the data we collect.
Whether it's online or offline, if we're not doing focus groups, we're usually using surveys to collect Primary Data. Surveys give us the opportunity to draw conclusions about different groups of consumers by studying a small statistical sample of the total consumer population. The "sample" is the key. A sample is usually defined as a segment of the population selected for our research that will represent the larger population as a whole. Whether or not a sample is good enough to make observations with, depends on how we've designed it.
Designing a sample is a three step process:
1) Decide who you are going to survey
2) Decide how many you are going to survey
3) Decide how you are selecting the participants in the sample
Let's examine each of these three steps a little more.
1) Decide who you are going to survey
First, you have to decide who you are actually going to survey. In more statistical terms, we are asking "what is the sampling unit"? Any group of people can be used as a sampling unit. What I mean here is children, adult women, men, etc. Your sampling unit should be determined by the target groups in your survey, and the data you have about your target customers. If you don't know who your target customer is, then you have some research to do first. Choosing the wrong sampling unit will waste your time and your money. It will give you data that you cannot use, because the results from that group will be irrelevant.
2) How many should be surveyed (what is the sample size)
When we are asking ourselves "how many should be surveyed", what we are saying here is "what is the sampling size?" Sample sizes that contain more people usually give us increased accuracy. For you statistical junkies, there are certain facts of mathematical statistics that describe this, such as the law of large numbers and the central limit theorem. To keep this simple for our discussion, larger samples will give you more statistically reliable results than smaller sample sizes. However, larger sample sizes will cost you more money. Do not assume that you need to attempt to sample an entire population segment (which would take forever, and be almost impossible). Usually less than 1 percent of a population segment will provide statistically reliable results. There is a down-side to Probability Samples: cost. Depending on your Contact Method, larger samples will result in drastically higher costs. When cost is a factor, then researchers turn to Non-Probability samples.
3) How should the people in the sample be selected?
What we are asking here is, "What is the sampling procedure we are going to follow?" There are two different types of samples we can choose from: Probability Samples, and Non-Probability Samples. Probability Samples give each population member (a.k.a. a potential participant) a possible chance of being included in the sample. Because you are not sampling the entire population, probability samples will always contain margin for error. The larger the margin of error, the less trust you can place in the data you have that is supposed to represent your "population". Larger samples give you less margin of error, and less margin of error lets you trust your data more.
There are three different types of Probability Samples:
Simple Random Sample
Every member of the population has a known and equal chance of selection.
Stratified Random Sample
The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups (such as age and race) and random samples are drawn from each group. Basically, you are splitting your population into defined groups, and then sampling each of those groups.
Cluster (area) Samples
The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups (such as blocks, and they are relatively homogeneous) and the researcher draws a simple random sample of each group.
Non-probability sampling is much less expensive than doing Probability Sampling, but the results are of limited value, because the data is less reliable. Non-probability samples should be used with caution. Non-probability sampling techniques cannot be used to deduce generalizations from the sample to the general population. Any generalizations created from a non-probability sample MUST be filtered through the researcher's knowledge (and yours) of the customer population being studied.
There are three different kind of Non-probability samples:
Convenience Sample
In a Convenience Sample, the researcher selects the "easiest", most convenient to locate member from the immediate population to obtain research data from. I would consider this one of the most hap-hazard methods. There is practically nothing you can generalize about the data you obtain, other than considering it a "snapshot" of a a particular group, at a particular time, at a particular place.
Judgment Sample
In a Judgment Sample, the researcher will use his/her judgement to select the the people sampled. Immediately you have to ask...how good is their judgment in selecting a good candidate? Again, the data that you obtain from this sort of sampling is just not reliable for generalized conclusions, but it may be interesting to use as a "snapshot".
Quota Sample
Probably the worst method I can think of, a Quota Sample is simply a researcher grabing enough people to meet a quota requirement for sampling participants. Stay away from this sort of methodology. Your data is practically useless.
Never select a sampling method without taking the time (as you always should) to weigh the needs you have when collecting Primary Data. Always take into consideration your time-frame and your budget, and always try to be as objective as possible when you are evaluating the Primary Data you have obtained.
Follow @macdailybites
Whether it's online or offline, if we're not doing focus groups, we're usually using surveys to collect Primary Data. Surveys give us the opportunity to draw conclusions about different groups of consumers by studying a small statistical sample of the total consumer population. The "sample" is the key. A sample is usually defined as a segment of the population selected for our research that will represent the larger population as a whole. Whether or not a sample is good enough to make observations with, depends on how we've designed it.
Designing a sample is a three step process:
1) Decide who you are going to survey
2) Decide how many you are going to survey
3) Decide how you are selecting the participants in the sample
Let's examine each of these three steps a little more.
1) Decide who you are going to survey
First, you have to decide who you are actually going to survey. In more statistical terms, we are asking "what is the sampling unit"? Any group of people can be used as a sampling unit. What I mean here is children, adult women, men, etc. Your sampling unit should be determined by the target groups in your survey, and the data you have about your target customers. If you don't know who your target customer is, then you have some research to do first. Choosing the wrong sampling unit will waste your time and your money. It will give you data that you cannot use, because the results from that group will be irrelevant.
2) How many should be surveyed (what is the sample size)
When we are asking ourselves "how many should be surveyed", what we are saying here is "what is the sampling size?" Sample sizes that contain more people usually give us increased accuracy. For you statistical junkies, there are certain facts of mathematical statistics that describe this, such as the law of large numbers and the central limit theorem. To keep this simple for our discussion, larger samples will give you more statistically reliable results than smaller sample sizes. However, larger sample sizes will cost you more money. Do not assume that you need to attempt to sample an entire population segment (which would take forever, and be almost impossible). Usually less than 1 percent of a population segment will provide statistically reliable results. There is a down-side to Probability Samples: cost. Depending on your Contact Method, larger samples will result in drastically higher costs. When cost is a factor, then researchers turn to Non-Probability samples.
3) How should the people in the sample be selected?
What we are asking here is, "What is the sampling procedure we are going to follow?" There are two different types of samples we can choose from: Probability Samples, and Non-Probability Samples. Probability Samples give each population member (a.k.a. a potential participant) a possible chance of being included in the sample. Because you are not sampling the entire population, probability samples will always contain margin for error. The larger the margin of error, the less trust you can place in the data you have that is supposed to represent your "population". Larger samples give you less margin of error, and less margin of error lets you trust your data more.
There are three different types of Probability Samples:
Simple Random Sample
Every member of the population has a known and equal chance of selection.
Stratified Random Sample
The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups (such as age and race) and random samples are drawn from each group. Basically, you are splitting your population into defined groups, and then sampling each of those groups.
Cluster (area) Samples
The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups (such as blocks, and they are relatively homogeneous) and the researcher draws a simple random sample of each group.
Non-probability sampling is much less expensive than doing Probability Sampling, but the results are of limited value, because the data is less reliable. Non-probability samples should be used with caution. Non-probability sampling techniques cannot be used to deduce generalizations from the sample to the general population. Any generalizations created from a non-probability sample MUST be filtered through the researcher's knowledge (and yours) of the customer population being studied.
There are three different kind of Non-probability samples:
Convenience Sample
In a Convenience Sample, the researcher selects the "easiest", most convenient to locate member from the immediate population to obtain research data from. I would consider this one of the most hap-hazard methods. There is practically nothing you can generalize about the data you obtain, other than considering it a "snapshot" of a a particular group, at a particular time, at a particular place.
Judgment Sample
In a Judgment Sample, the researcher will use his/her judgement to select the the people sampled. Immediately you have to ask...how good is their judgment in selecting a good candidate? Again, the data that you obtain from this sort of sampling is just not reliable for generalized conclusions, but it may be interesting to use as a "snapshot".
Quota Sample
Probably the worst method I can think of, a Quota Sample is simply a researcher grabing enough people to meet a quota requirement for sampling participants. Stay away from this sort of methodology. Your data is practically useless.
Never select a sampling method without taking the time (as you always should) to weigh the needs you have when collecting Primary Data. Always take into consideration your time-frame and your budget, and always try to be as objective as possible when you are evaluating the Primary Data you have obtained.
Follow @macdailybites
Tuesday, August 14, 2012
Marketing 101: Primary Data - Contact Methods
In my last Marketing 101 piece, I spent some time introducing the Research Methods that we typically use in Primary Data collection. Remember that Research Methods consist of surveys, experimentation and observation. Surveys are the workhorse of Primary Data collection. They tend to give us the bulk of our information related to customer trends and buying behaviors. In order to conduct these surveys, information is collected in a variety of manners. Typically these Contact Methods include mail, telephone, focus groups, and various other online technologies.
Mail
The mailed questionnaire is a classic primary data collection method. It is very valuable, because it can be used to collect massive amounts of primary data for a very low cost per respondent. We're talking the cost of paper and postage. (Remember that you do need to calculate the labor costs of crafting the survey and processing the data once it comes back to you) The data that you can collect from mail methods is usually considered very good for a few reasons. First, there is little chance for "interviewer bias", because there is no live person there to ask the questions in a manner that could influence a person to respond in a manner different than they normally would. Second, because they are not being interviewed in person, the respondents are usually more willing to give more honest responses. And third, because you are not relying on the interviewer to record responses, no interviewer bias is introduced to the answers.
However there are downsides to using mail as a contact method. First, mail-based surveying is not very flexible, because all respondents are required to approach their surveys in the same way. Second, collecting primary data via mail is very slow. It can take months before a reasonable amount of your sample sends the questionnaires back to you for processing. Third, because written surveys usually take longer to complete, the response rate trends lower - simply because it takes more work. The response rate is actually considred to be very fair. It's harder to control the sample, beacuse you don't know which households will respond, let alone who at the residence will respond.
Telephone
Telephone has always been a fairly good method of collecting Primary Data. First, it is possible to collect massive amounts of data very quickly by using multiple people at the same time to call and conduct phone interviews everyday. Second, telephone interviews allow for more flexibility, because your interviewers have the opportunity to provide clarity about any questions that respondents don't understand. Third, you have excellent control of the sample, because interviewers can screen out callers before an interview is conducted. Fourth, with the right incentives, typically the response rate is actually very good.
There are problems with collecting Primary Data via telephone as well. First, the quality of the data you collect can only be considered fair at times, because the interviewer can inadvertently introduce bias into the answers based on how the questions are asked. Second, because the respondents are interacting with a live person, they may not want to provide completely honest answers to questions that they may consider too private. Third, telephone surveys are more expensive, because they require more labor.
Focus Groups
Focus Groups are a Primary Data collection standard. Focus Groups have become a leading method for gaining valuable insight into consumer thoughts and feelings and their buying behaviors. Traditionally focus groups consist of a moderator leading six to ten people. However technology has allowed focus groups to be conducted through video conferencing and webinars via the internet, which allows people from different locations to be connected together which can improve sampling. These groups will participate in discussions about products, advertisements, services, and even organizations. The focus group attendees are usually paid a small sum for attending. The moderator will attempt to lead an easy and free flowing discussion hoping that free honest responses will be given. Data is usually recorded by the moderator, however sometimes focus groups are observed by staff members via cameras or through one-way windows.
Focus groups also have their issues. First, focus groups use much smaller sample sizes in order to control cost and keep their sizes manageable. Second, because sample sizes are so small, it is hard to reliably statistically generalize the results. Third, attendees of focus groups are not always candid and honest. The phyiscal and sociological environment of the focus group can create peer pressure, which leads attendees to alter their results in order to "fit in" with the people surrounding them. This is being combated by using environments that are relevant to the products and services being studied in order to get more relevant and open responses. Fourth, focus groups cost much much more to conduct due to the costs of time, labor, location, and data acquisition. Only use focus groups when it is appropriate and you are looking for specific types of data that you cannot reliably acquire with other Contact Methods.
Online Methods
The internet has single-handedly changed the Primary Data landscape. Researchers are no longer confined to using mail, telephone, or physically location-bound focus groups. There are many electronic alternatives to all three primary contact methods.
Email surveys and survey research websites are very affordable alternatives to direct mail and telephone interviews. Because they are electronic, they are much less expensive to conduct, and data is instantly stored into a database that can be manipulated and analyzed. It is also quicker to create a large sampling, because your contact list can be created by interfacing with your existing customer database, or by purchasing lists of consumers from secondary data companies. As with mail, the quality of responses tends to be very good, because it is an impersonal process and respondents feel more open to share more "private" information.
Another alternative to the telephone or physical focus group collection methods is Skype, or any other video conferencing type of technology. Because Skype and services such as Oovoo are available for free or very little cost, it is much less expensive to conduct focus group research when the researcher needs to observe the reactions of the attendees. These services will usually have the ability to record online "meetings", which allows you to store and refer back to interviews easily.
No matter what contact method you choose to use in your Primary Data collection process, it is important to spend extensive time up front evaluating the type of data you need, and which methods fit your required data types, cost, and schedule.
Follow @macdailybites
The mailed questionnaire is a classic primary data collection method. It is very valuable, because it can be used to collect massive amounts of primary data for a very low cost per respondent. We're talking the cost of paper and postage. (Remember that you do need to calculate the labor costs of crafting the survey and processing the data once it comes back to you) The data that you can collect from mail methods is usually considered very good for a few reasons. First, there is little chance for "interviewer bias", because there is no live person there to ask the questions in a manner that could influence a person to respond in a manner different than they normally would. Second, because they are not being interviewed in person, the respondents are usually more willing to give more honest responses. And third, because you are not relying on the interviewer to record responses, no interviewer bias is introduced to the answers.
However there are downsides to using mail as a contact method. First, mail-based surveying is not very flexible, because all respondents are required to approach their surveys in the same way. Second, collecting primary data via mail is very slow. It can take months before a reasonable amount of your sample sends the questionnaires back to you for processing. Third, because written surveys usually take longer to complete, the response rate trends lower - simply because it takes more work. The response rate is actually considred to be very fair. It's harder to control the sample, beacuse you don't know which households will respond, let alone who at the residence will respond.
Telephone
Telephone has always been a fairly good method of collecting Primary Data. First, it is possible to collect massive amounts of data very quickly by using multiple people at the same time to call and conduct phone interviews everyday. Second, telephone interviews allow for more flexibility, because your interviewers have the opportunity to provide clarity about any questions that respondents don't understand. Third, you have excellent control of the sample, because interviewers can screen out callers before an interview is conducted. Fourth, with the right incentives, typically the response rate is actually very good.
There are problems with collecting Primary Data via telephone as well. First, the quality of the data you collect can only be considered fair at times, because the interviewer can inadvertently introduce bias into the answers based on how the questions are asked. Second, because the respondents are interacting with a live person, they may not want to provide completely honest answers to questions that they may consider too private. Third, telephone surveys are more expensive, because they require more labor.
Focus Groups
Focus Groups are a Primary Data collection standard. Focus Groups have become a leading method for gaining valuable insight into consumer thoughts and feelings and their buying behaviors. Traditionally focus groups consist of a moderator leading six to ten people. However technology has allowed focus groups to be conducted through video conferencing and webinars via the internet, which allows people from different locations to be connected together which can improve sampling. These groups will participate in discussions about products, advertisements, services, and even organizations. The focus group attendees are usually paid a small sum for attending. The moderator will attempt to lead an easy and free flowing discussion hoping that free honest responses will be given. Data is usually recorded by the moderator, however sometimes focus groups are observed by staff members via cameras or through one-way windows.
Focus groups also have their issues. First, focus groups use much smaller sample sizes in order to control cost and keep their sizes manageable. Second, because sample sizes are so small, it is hard to reliably statistically generalize the results. Third, attendees of focus groups are not always candid and honest. The phyiscal and sociological environment of the focus group can create peer pressure, which leads attendees to alter their results in order to "fit in" with the people surrounding them. This is being combated by using environments that are relevant to the products and services being studied in order to get more relevant and open responses. Fourth, focus groups cost much much more to conduct due to the costs of time, labor, location, and data acquisition. Only use focus groups when it is appropriate and you are looking for specific types of data that you cannot reliably acquire with other Contact Methods.
Online Methods
The internet has single-handedly changed the Primary Data landscape. Researchers are no longer confined to using mail, telephone, or physically location-bound focus groups. There are many electronic alternatives to all three primary contact methods.
Email surveys and survey research websites are very affordable alternatives to direct mail and telephone interviews. Because they are electronic, they are much less expensive to conduct, and data is instantly stored into a database that can be manipulated and analyzed. It is also quicker to create a large sampling, because your contact list can be created by interfacing with your existing customer database, or by purchasing lists of consumers from secondary data companies. As with mail, the quality of responses tends to be very good, because it is an impersonal process and respondents feel more open to share more "private" information.
Another alternative to the telephone or physical focus group collection methods is Skype, or any other video conferencing type of technology. Because Skype and services such as Oovoo are available for free or very little cost, it is much less expensive to conduct focus group research when the researcher needs to observe the reactions of the attendees. These services will usually have the ability to record online "meetings", which allows you to store and refer back to interviews easily.
No matter what contact method you choose to use in your Primary Data collection process, it is important to spend extensive time up front evaluating the type of data you need, and which methods fit your required data types, cost, and schedule.
Follow @macdailybites
Tuesday, July 31, 2012
Marketing 101: Primary Data Collection - Research
In this edition of the Marketing 101 series we will take a quick look at Primary Data collection. So far we have been discussing data that is considered secondary. Secondary data was collected by someone else. Whether it was your sales department, or a comScore research report that you purchased, it was created by someone else other than your department. It did not involve any of your department interacting with existing and potential customers to collect data. It was not collected with your marketing objectives in mind.
There is nothing wrong with secondary data. You cannot perform any Market Intelligence without secondary data. It is a great and necessary starting point for any of your research. Secondary data is critical when you are defining the problems and objectives that are the focus of your Marketing Intelligence initiatives. However in most cases, you will need to collect primary data of some kind in order to have the information you need to make real decisions.
What is Primary Data?
Primary Data is research that has been conducted by your organization, first hand. It is also known as Field Research. It is usually more reliable than secondary data, because it is usually more accurate since you collected it yourself. Primary data is specific and relevant to your products and services. However, Primary Data is often very time consuming to collect, and usually costs more to create than purchasing secondary data reports. You must take special care when collecting primary data. It needs to be relevant, current, and as unbiased as possible.
Primary Data is relevant when it directly applies to your company's products and services. It is relevant when it relates to the problems you are trying to solve, and the marketing goals of your organization. Primary Data is current when it is recent, and directly corresponds to the profile of your customers TODAY. Primary Data is unbiased when your subjects have been honest and open during data collection. When constructing your Primary Data collection plan, you must consider research methods, contact methods, the sampling plan, and your research instruments.
Research Methods consist of observation, surveys, and experimentation. Contact Methods typically consist of mail, phone, personal interaction, and various online methods. Sampling Plans take into account units, size, and procedures. Research Instruments typically consist of questionnaires and other mechanical instruments. Let's start with a quick discussion of Research Methods. There are three typical ways that Primary Data is collected in marketing: observation, surveys, and experiments.
Observation
Observation is the collection of Primary Data through observing people, their actions and the situations they are in. Observation may be the easiest research to do. Typically, observation is also the most cost effective method. Observation can also give you data that people aren't usually willing to tell you themselves, such as their feelings, emotions, attitudes or the motives behind their buying decisions.
How does observation work? It's extremely simple. Take a restaurant franchise owner. He may be planning on opening another location. He may also have little or no money to pay for marketing research. However a lot of the data he needs he can collect himself. He can get into his car and drive around town, observing the traffic patterns. He can see where his clientele goes to shop. He can see what time the traffic appears. He can call real estate agents and ask them for lease prices for different properties. He can drive around and look for areas that don't have his type of restaurant, looking for areas of little competition. He can do all of this for just the cost of the gas in his car. You can do this yourself.
Surveys
Surveys are the most common method of collecting Primary Data. Surveys are the best way to get the descriptive information that you need for your marketing intelligence. Simply put, surveys collect data by asking other people a series of questions about their personal knowledge, emotions, attitudes, preferences, and buying behaviors. Surveys can provide you a wealth of data. There is always a golden nugget, a piece of data that can give you the insight you need to figure out the direction of your next campaign.
However, there are drawbacks to the data you collect via surveys. Often people just don't recall some of the information that you are asking for, and as a result, they are unable to answer the questions. Therefore the response that they give will not be the complete truth, it may be something that they feel you want to hear. Sometimes people are unwilling to provide information that they might deem "private". This prevents completely truthful responses, and it skews the data that you are analyzing. If the responses seem too good to be true...they just may be.
Experimentation
Primary Data can also be collected via experimentation. Experimentation is the practice of gathering data by selecting matched groups of people, giving them different treatments or scenarios, controlling related factors in their environments, and checking for differences in their responses. Experimentation gives us what we call "causal" data. Causal data helps us explain cause and effect relationships. Experimenting helps us try to answer "why" someone is doing something, and what influences their buying behavior.
A common example of experimentation is price testing. To the buyer, price will be the final emotional factor that determines whether or not they will give us their hard earned money. Depending on the product and market segment, price may be the most important factor. How do you know what price is the right price? You have to test it. Many companies will test certain prices when collecting primary data on a new menu item that is being developed. How do you think McDonalds knows how much to charge for a Big Mac? They tested how much they can charge for that Big Mac, looking for that magic number that will provide the most sales and the most profit.
In my next post we will continue this exploration of Primary Data by examining different contact methods.
Follow @macdailybites
There is nothing wrong with secondary data. You cannot perform any Market Intelligence without secondary data. It is a great and necessary starting point for any of your research. Secondary data is critical when you are defining the problems and objectives that are the focus of your Marketing Intelligence initiatives. However in most cases, you will need to collect primary data of some kind in order to have the information you need to make real decisions.
What is Primary Data?
Primary Data is research that has been conducted by your organization, first hand. It is also known as Field Research. It is usually more reliable than secondary data, because it is usually more accurate since you collected it yourself. Primary data is specific and relevant to your products and services. However, Primary Data is often very time consuming to collect, and usually costs more to create than purchasing secondary data reports. You must take special care when collecting primary data. It needs to be relevant, current, and as unbiased as possible.
Primary Data is relevant when it directly applies to your company's products and services. It is relevant when it relates to the problems you are trying to solve, and the marketing goals of your organization. Primary Data is current when it is recent, and directly corresponds to the profile of your customers TODAY. Primary Data is unbiased when your subjects have been honest and open during data collection. When constructing your Primary Data collection plan, you must consider research methods, contact methods, the sampling plan, and your research instruments.
Research Methods consist of observation, surveys, and experimentation. Contact Methods typically consist of mail, phone, personal interaction, and various online methods. Sampling Plans take into account units, size, and procedures. Research Instruments typically consist of questionnaires and other mechanical instruments. Let's start with a quick discussion of Research Methods. There are three typical ways that Primary Data is collected in marketing: observation, surveys, and experiments.
Observation
Observation is the collection of Primary Data through observing people, their actions and the situations they are in. Observation may be the easiest research to do. Typically, observation is also the most cost effective method. Observation can also give you data that people aren't usually willing to tell you themselves, such as their feelings, emotions, attitudes or the motives behind their buying decisions.
How does observation work? It's extremely simple. Take a restaurant franchise owner. He may be planning on opening another location. He may also have little or no money to pay for marketing research. However a lot of the data he needs he can collect himself. He can get into his car and drive around town, observing the traffic patterns. He can see where his clientele goes to shop. He can see what time the traffic appears. He can call real estate agents and ask them for lease prices for different properties. He can drive around and look for areas that don't have his type of restaurant, looking for areas of little competition. He can do all of this for just the cost of the gas in his car. You can do this yourself.
Surveys
Surveys are the most common method of collecting Primary Data. Surveys are the best way to get the descriptive information that you need for your marketing intelligence. Simply put, surveys collect data by asking other people a series of questions about their personal knowledge, emotions, attitudes, preferences, and buying behaviors. Surveys can provide you a wealth of data. There is always a golden nugget, a piece of data that can give you the insight you need to figure out the direction of your next campaign.
However, there are drawbacks to the data you collect via surveys. Often people just don't recall some of the information that you are asking for, and as a result, they are unable to answer the questions. Therefore the response that they give will not be the complete truth, it may be something that they feel you want to hear. Sometimes people are unwilling to provide information that they might deem "private". This prevents completely truthful responses, and it skews the data that you are analyzing. If the responses seem too good to be true...they just may be.
Experimentation
Primary Data can also be collected via experimentation. Experimentation is the practice of gathering data by selecting matched groups of people, giving them different treatments or scenarios, controlling related factors in their environments, and checking for differences in their responses. Experimentation gives us what we call "causal" data. Causal data helps us explain cause and effect relationships. Experimenting helps us try to answer "why" someone is doing something, and what influences their buying behavior.
A common example of experimentation is price testing. To the buyer, price will be the final emotional factor that determines whether or not they will give us their hard earned money. Depending on the product and market segment, price may be the most important factor. How do you know what price is the right price? You have to test it. Many companies will test certain prices when collecting primary data on a new menu item that is being developed. How do you think McDonalds knows how much to charge for a Big Mac? They tested how much they can charge for that Big Mac, looking for that magic number that will provide the most sales and the most profit.
In my next post we will continue this exploration of Primary Data by examining different contact methods.
Follow @macdailybites
Sunday, July 22, 2012
Marketing 101: Marketing Intelligence: External Data Sources
 When conducting Marketing Intelligence you will need to explore External Data sources. Here is a list of popular paid and free external data sources.
When conducting Marketing Intelligence you will need to explore External Data sources. Here is a list of popular paid and free external data sources. ACNielsen Corporation
www.nielsen.com/us/
In 100 countries around the world, Nielsen provides clients the most complete understanding of what consumers watch and buy. Provides television audience data along with supermarket scanner data on sales, market share, retail prices, and household purchases.
Ad Age Datacenter
http://adage.com/datacenter/
AdAge.com's DataCenter features premium content, including profiles of top advertisers, media, agencies and more.
American Demographics
American Demographics creates reports on demographic trends and their significance.
Arbitron
www.arbitron.com
Arbitron provides local radio market and internet radio audience data, along with advertising expenditure information data.
ClickZ Stats/CyberAtlas
www.clickz.com
Provides information about internet use by consumers, such as e-commerce statistics.
comScore Networks
www.comscore.com
comScore provides consumer behavior information and geo-demographic analysis of internet use. They also have large amounts of data about digital media use around the world.
Dun & Bradstreet
www.dnb.com
D&B maintains a massive database with information on over 50 million individual companies around the globe.
Factiva
global.factiva.com
Factiva offers business and knowledge management solutions, and competitive intelligence data. They specialize in in-depth financial, historical, and operational data on public and private companies.
Federal Trade Commission
www.ftc.gov
The FTC website provides information on regulations and decisions related to consumer protection and antitrust laws in the United States.
Forrester Reasearch (Acquired Jupiter Research)
www.forrester.com/home
Forrester Research monitors internet traffic and provides rankings on the most popular sites.
Hoovers, Inc.
www.hoovers.com
Hoovers provides business descriptions, financial overviews, and news about major companies around the world.
IMS Health
www.imshealth.com
IMS Health specializes in tracking drug sales, monitoring performance of pharmaceutical sales representatives, and offers pharmaceutical market forecasting data.
Interactive Advertising Bureau
www.iab.net
iab creates statistics about advertising on the internet.
J.D. Power and Associates
www.jdpower.com
J.D. Power and Associates provides information via independent consumer surveys of product and service quality, customer satisfaction, and buyer behavior.
LexisNexis
www.lexisnexis.com
LexisNexis features articles from business, consumer, and marketing publications, and tracks firms, industries, trends, and promotion techniques.
NetBase
www.netbase.com
Offers social media analysis tools that help marketing and sales professionals analyze consumer insights, opinion, emotion, and behavior online.
Securities and Exchange Commission Edgar Database
www.sec.gov/edgar.shtml
This SEC database provides financial data on U.S. public corporations.
Simmons Market Research Bureau
www.simmonssurvey.com
Provides detailed analysis of consumer patterns in 400 product categories in selected markets.
SocialBakers
http://analytics.socialbakers.com/
SocialBakers is a premiere provider of social media metrics and analytics tools.
Stat-USA
This popular Department of Commerce site, highlighting statistics on U.S. business and international trade was closed in 2010. Various websites provide links to all of the data that was hosted there.
http://library.apsu.edu/inform/21STAT-USAtransition.htm (Felix G Woodard Library)
SymphonyIRI (formerly Information Resources, Inc.)
www.symphonyiri.com
Provides supermarket scanner data for tracking grocery product movement and new product purchasing data.
Thomson Dialogwww.dialog.com
Thomson Dialog offers access to more than 900 database containing publications reports newsletters and directories covering dozens of industries.
U.S. Census
www.census.gov
The U.S. Census provides detailed statistics and trends about the U.S. population
U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
www.uspto.gov
This U.S. government agency allows searches to find out who has filed for trademarks and patents across the United States.
Follow @macdailybites
Tuesday, July 10, 2012
Marketing 101: Developing Marketing Information
Next in our discussion of Marketing Information Systems, we're going to explore Developing Marketing Information. Marketing Information Systems rely on multiple types of marketing data. As a Marketing Manager, you need to stay on top of creating and maintaining these data sources that are vital to your ability to make strategic marketing decisions. You can obtain the data you need from internal databases, marketing intelligence, and marketing research.
Internal Data Sources
Internal Data is usually your first stop when doing marketing research. Internal data consists of your collections of electronic data. This data contains consumer and marketing information, and it is usually created from existing data sources inside your own business. This data comes from numerous sources. Your accounting department keeps records of sales, costs and cash flows. Your operations department will have data on production schedules, logistics, and staffing. Your own marketing department will have information on your customers, their transactions, their demographics, psychographics, and buying behaviors. Your customer service representatives will have data on customer satisfaction, and any service issues that they deal with. (Side note: if you do not have anyone devoted to customer service in your business, seriously think about hiring someone) Your sales department has tons of valuable information. They will have reports on your resellers, activity of your competitors, and your channel partners will have data on point-of-sale transactions. All of this data can be found inside of your Marketing Micro-environment.
Internal data is usually faster to get ahold of, and much cheaper to use, but there are potential issues to be aware of. First, your own internal data may be incomplete, and it might not contain the data you really need. Second, often that data is not in the right form you need to use it. For example, sales data usually will need to be converted from existing financial reports into a format that can be used for evaluating your customer segments, your sales force, or your channel performance. Third, data ages quickly. In fact, it ages immediately. It is always old. Data is only as fresh as that date it was collected. Keeping data current takes a lot of man power and time to update. There must be a staff person dedicated to this task at all times. Fourth, managing your data requires data backup, higher end PC's for transforming data, and more advance reporting techniques depending on how you want to look at your data.
External Data Sources
Eventually you will run out of usable data inside your own walls. Inevitably you will have to do some additional research, depending on the data requirements you have, and the reports you are looking to create. It's time to do some Marketing Intelligence. Marketing Intelligence is the systematic collection and analysis of publically available information about your competitors and other developments in the marketplace. Marketing Intelligence aims to improve your strategic decision making, helps you assess and track your competitors actions, and can give you an early alert of new opportunities and potential threats coming from outside your own walls.
The practice of, and the "art" of Marketing Intelligence, has grown exponentially as more businesses are "spying" on their competitors. Common Marketing Intelligence practice has grown to include interviewing competitors staff, benchmarking competitor's products, doing research online, attending trade shows, and even some occassional dumpster diving. There is also a wealth of publically available information online. You can monitor publically published information - such as product reviews, SEC filings, pubically available financial records, annual reports, business publications (corporate magazines that go to partners), press releases, advertisements, and competitor's websites. It is also possible to acquire information from competitor's suppliers, your own resellers, and competitor's major customers. All of this information provides a wealth of information about your competitor's strategies, markets, new products, and other company happenings.
In my next post I will cover a number of free and paid database services that you can use in your marketing intelligence endevors.
Follow @macdailybites
Wednesday, July 4, 2012
Marketing 101: Managing Marketing Information: An Overview
Now that we have finished our overview of the Marketing Micro-environment, it's time to begin looking at Managing Marketing Information.
Why do we care about marketing information? Marketing Information allows the Marketing Manager to do their job; it allows them to make real strategic decisions involving a business's brand, it's products, and the messages communicated to it's Publics. Marketing Information provides a business with data about it's customers needs, the marketing environment, and it's competition. A Marketing Information System provides data to key partners and suppliers in the Marketing Micro-environment. Marketing managers usually need more information, they need the right information.
Over the next few weeks during out discussion of Managing Marketing Information we are going to cover:
- Assessing Marketing Needs
- Developing Marketing Information
- Marketing Research
- Analyzing Marketing Information
Assessing Marketing Needs
A good Marketing Information System balances the information you would LIKE to have with the information you NEED to have. Remember, you don't need more information, just the RIGHT information. Your responsibility as a marketing manager is to interview your staff to find out these needs. Sometimes they may ask for more than they need, and they may not ask for what they really need because they don't know they need it. Some managers won't ask for certain types of information because they feel they should already know it.
Sometimes it's not possible for your business to provide the information you need, because it is not available, or it is not capable because of your current Marketing Information System's limitations. Always consider that the costs of obtaining, processing, storing and delivering marketing information can quickly become prohibitive for many business's. You must decide if the benefits of having more information are worth the costs of providing it to your staff. However, this can be hard to assess. Remember that information doesn't itself have value. What gives data value is how you are using it and the results it is providing your business.
Wednesday, June 6, 2012
Marketing 101: Microenvironment - Publics
This week's Marketing 101 is going to continue on in Marketing Microenvironments. Today we are focusing on Publics.
In simple terms, a Public is any group of people that may have an real or potential interest in ... or an impact on ... your business's ability to achieve its objectives - whatever they may be. Why should you care about Publics? It's simple. Publics can help, or hinder your ability to get your message out to your customers, and collect value from them.
Financial Publics
Your relationships with Financial Publics are extremely important. These relationships directly influence your ability to obtain funding for your business. Financial Publics typically include banks, investment houses and stock holders. How these groups perceive you will directly affect your ability to get loans, favorable payment terms, and whether or not other Publics choose to do business with you. For example, if a brokerage perceives that you are having issues internally, or your products have deficiencies, then it may give your stock a low rating. If that happens, people may sell your stock, your market valuation will decrease, and your customers may start to buy less of your products and services.
Media Publics
Media Publics can be extremely valuable, or they can be a thorn in your side. Media Publics typically carry news, features and editorial opinions, delivering them to your customers and other Publics. They include newspapers, blogs, magazines (print and digital), radio (broadcast and internet) and television outlets (broadcast and digital). You can carry out your "relationship" with Media Publics via VNR's, PR media releases, op ed's, interviews, or open invitations to review your products and services. Do not be afraid to make friends and connect with people in the media. You can gently influence what they say about you. Having a good relationship with people in the media can make a bad situation for your company "tolerable" or a PR disaster in the eyes of your customers.
Government Publics
Take note: Management MUST take governmental developments into account. You should always keep an eye on the current state of any laws and regulations that effect the production of your products, the day-to-day operation of your business, or the methods you can use to sell your products and services. Marketers must often consult with government officials, their lawyers, and sometimes lobbyists. Get to know your local government, and keep tabs on what your government officials are doing.
Citizen-Action Publics
The decisions you make will sometimes be questioned by citizens, consumer organizations, environmental groups, minority groups and others. Your PR department can help you stay in touch with these groups. It can keep you abreast of any concerns or problems that arise. Make it your mission to get to know the citizen groups that may affect your business and your marketing practices. Make it a point to have a friendly relationship with any of their representatives.
Local Publics
Local Publics typically include neighborhood residents and community organizations. Businesses will usually appoint a community relations officer to meet with the community, answer questions and contribute to worthwhile causes.
General Publics
A business needs to be concerned with the general public's attitude and perception towards its products and activities in the marketplace. The perception of the business, it's brands, products and services in the public directly effect consumers buying habits. Keep an eye on Twitter feeds and FaceBook posts. You will be able to get a very real sense of the general public's perception of you in the marketplace.
Internal Publics
Internal Publics are groups of people inside your own business. These groups can consist of employees, managers, volunteers, and the board of directors. Businesses typically use newsletters, memos, company meetings, intranets and other means to motivate and educate their internal publics. When your employees feel good working for you, when your board of directors are happy with your success, when your internal communications send the right messages to motivate, encourage, train, and edify your staff, this positive attitude spills over to external publics, and helps to communicate your brand message in the marketplace.
A business can construct strategic marketing plans for some or all of these major Publics alongside it's chosen customer markets. Suppose a business wants to evoke a specific response from a particular Public, such as donations of time or money (Cause Marketing). The business would have to design an messaging campaign for this Public that is enticing and persuading enough to coax the desired response.
Is it realistic for all businesses to pay attention to all of these Publics at the same time? No. Can you effectively market to all Publics. Yes and No. You have to make the judgement where to spend your time and resources. However, at some point in time you will have to deal with each of these Publics in some capacity. It is in your best interest to at least get to know them, and when appropriate, take action.
Follow @macdailybites
Tuesday, May 22, 2012
Marketing 101: The Microenvironment - Competitors
I want to start this week's post with a bit of caution: even though there may not be a lot to write, this part of the Micro-environment is by no means small or light. In fact, it is complex, requires a lot of thought and study, and must be properly evaluated. It's your Competitors.
The marketing concept states that in order for your marketing to be successful, your business must provide greater customer value and satisfaction that your competitors. In other words, you must do more than simply adapt to the needs of your target customers. Let me state this again: You must do more than just give your customers what you think they need, or they say they need. You must gain a strategic advantage by positioning your products and services against your competitors in the minds of your customers.
This is all about positioning. You have to differentiate yourself from your competitors.
You can't do this unless you study your competition. You have to study them, their products, their marketing messages, and figure out how to stand out above them.
This takes time and a lot of studying.
Remember, no single competitive marketing strategy is best for all companies and situations. You need to take into account your size and position compared to your competitors. Large firms with dominant positions in an industry can use certain strategies that smaller firms don't have the ability to from a resource standpoint (money and manpower). But being large is not enough. There are winning and losing strategies for all sized businesses. Small businesses must find the strategies that give them larger rates of return.
When is the last time you took a hard look at your competition?
Follow @macdailybites
Tuesday, May 15, 2012
Marketing 101: The Micro-environment - Customers
Next in the Marketing Micro-environment, we come to Customers.
Customers are the key to sales. If you don't have customers, you can't sell anything. Managers must continually study customer needs and try to anticipate how they are developing so they can meet these needs effectively now and in the future. However not all customers are the same. Managers must actively study five distinct categories of customer markets.
Consumer Markets
Consumer Markets are made up of individuals and household units. These customers buy products and services for their own personal use.
Business Markets
Customers in Business Markets typically purchase products and services that will be further processed or used in their own internal business processes. These customers are commonly referred to as B2B, or business-to-business customers.
Resellers
Customers in Reseller markets purchase products and services specifically to resell them to others for a profit. Well known resellers in the United States are "big box" stores, such as Target or Walmart.
Government Markets
Customers in Government Markets consist of government agencies that purchase products and services from private companies, and provide public services or transfer products and services to others who they deem need them. Some industries are much more dependent on Government Markets than others.
International Markets
Customers in International Markets are buyers who reside in other countries. These buyers include consumers, producers, resellers and even governments.
A business will typically sell it's products and services to multiple Customer Markets. Customer markets can also provide areas for a business to grow into. Each market requires it's own special strategic marketing to properly "sell" to it's distinct type of customer. Each Customer tastes and preferences will also change at different rates, and are effected by larger economic factors in different ways at different times. A good marketing manager will always have a good sense of what is going on in each of the Customer markets he or she is strategically marketing to.
Follow @macdailybites